-
Functional Areas
- Audit and Investigations
-
Capacity development and transition, strengthening systems for health
- A Strategic Approach to Capacity Development
- Capacity Development and Transition - Lessons Learned
- Capacity development and Transition Planning Process
- Capacity Development and Transition
- Capacity Development Objectives and Transition Milestones
- Capacity Development Results - Evidence From Country Experiences
- Functional Capacities
- Interim Principal Recipient of Global Fund Grants
- Legal and Policy Enabling Environment
- Overview
- Resilience and Sustainability
- Transition
-
Financial Management
- CCM Funding
- Grant Closure
- Grant Implementation
- Grant-Making and Signing
- Grant Reporting
- Import duties and VAT / sales tax
- Overview
- Sub-recipient Management
-
Grant closure
- Overview
-
Steps of Grant Closure Process
- 1. Global Fund Notification Letter 'Guidance on Grant Closure'
- 2. Preparation and Submission of Grant Close-Out Plan and Budget
- 3. Global Fund Approval of Grant Close-Out Plan
- 4. Implementation of Close-Out Plan and Completion of Final Global Fund Requirements (Grant Closure Period)
- 5. Operational Closure of Project
- 6. Financial Closure of Project
- 7. Documentation of Grant Closure with Global Fund Grant Closure Letter
- Terminology and Scenarios for Grant Closure Process
- Human resources
- Human rights, key populations and gender
-
Legal Framework
- Agreements with Sub-recipients
- Agreements with Sub-sub-recipients
- Amending Legal Agreements
- Implementation Letters and Performance Letters
- Language of the Grant Agreement and other Legal Instruments
- Legal Framework for Other UNDP Support Roles
- Other Legal and Implementation Considerations
- Overview
- Project Document
- Signing Legal Agreements and Requests for Disbursement
-
The Grant Agreement
- Grant Confirmation: Conditions Precedent (CP)
- Grant Confirmation: Conditions
- Grant Confirmation: Face Sheet
- Grant Confirmation: Schedule 1, Integrated Grant Description
- Grant Confirmation: Schedule 1, Performance Framework
- Grant Confirmation: Schedule 1, Summary Budget
- Grant Confirmation: Special Conditions (SCs)
- Grant Confirmation
- UNDP-Global Fund Grant Regulations
-
Monitoring and Evaluation
- Differentiation Approach
- Monitoring and Evaluation Components of Funding Request
- M&E Components of Grant Implementation
- Monitoring and Evaluation Components of Grant Making
- Overview
- Principal Recipient Start-Up
-
Health Product Management
- Compliance with the Global Fund requirements
- Distribution
- Inspection and Receipt
- International freight, transit requirements and use of INCOTERMS
- Inventory Management
- Overview
- Pharmacovigilance
- Product Selection
- Quality monitoring of health products
- Quantification and Forecasting
- Rational use
- Risk Management for PSM of health products
-
Sourcing and regulatory aspects
- Development of List of Health Products
- Development of the Health Procurement Action Plan (HPAP)
- Guidance on donations of health products
- Health Procurement Architecture
- Local Procurement of health products
- Other Elements of the UNDP Procurement Architecture
- Procurement of non-pharmaceutical Health Products
- Procurement of Pharmaceutical Products
- Submission of GHSC CO Procurement Request Form
- Storage
- Supply Planning of Health Products
- UNDP Health PSM Roster
- Waste management
- Grant Reporting
-
Risk Management
- Introduction to Risk Management
- Overview
- Risk management in crisis settings
-
Risk Management in the Global Fund
- Additional Safeguard Policy
- Challenging Operating Environment (COE) Policy
- Global Fund Review of Risk Management During Grant Implementation
- Global Fund Risk Management Framework
- Global Fund Risk Management Requirements During Funding Request
- Global Fund Risk Management Requirements for PRs
- Local Fund Agent
- Risk management in UNDP
- Risk Management in UNDP-managed Global Fund projects
- UNDP Risk Management Process
- Sub-Recipient Management
Cycle of Sub-recipient Monitoring
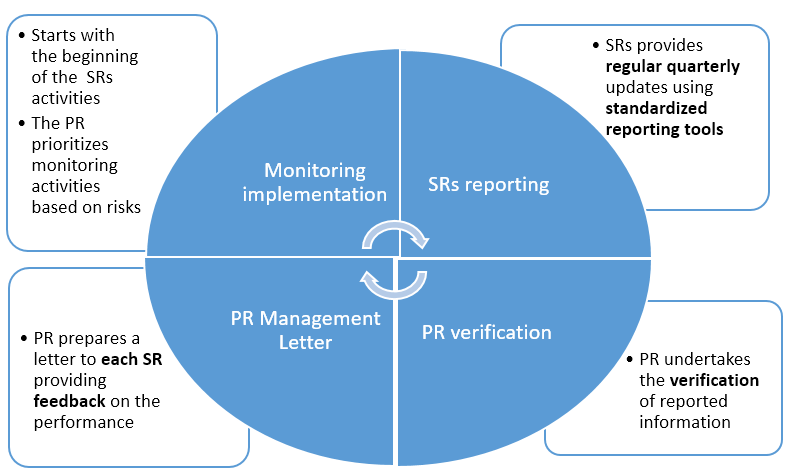
- Monitoring implementation: The cycle of Sub-recipient (SR) performance monitoring starts with the beginning of the activities implemented by the SR. The Principal Recipient (PR) should adopt a risk-based approach to prioritize the SRs, sites and activities to supervise based on the SR assessment, the importance of a site in regard to project performance, volume of funds and/or commodities managed by an SR and the risk related to the implementation of a specific activity. Following each monitoring activity, the PR should provide feedback in order to allow timely correction and improve implementation.
- SR reporting: SRs provide regular quarterly updates using standardized reporting tools to record the programmatic and financial achievement of the quarter.
- PR verification: As the third step, the PR undertakes the verification of reported financial information, inventory of health commodities (where applicable) and programmatic results. The verification is a team effort and part of it can take place on PR premises (reviewing the supporting documentation provided by SRs) and, if required, at the SR’s office according to the process previously described. The PMU should plan the data verification within a week after reception of the SR report to allow timely reporting of the PR to the Global Fund. Each Programme Management Unit (PMU) unit works with its contact person at SR level.
-
PR Management Letter: It is good practice, after review and verification of SR reports, for the PR to prepare a letter to each SR providing feedback on the SR’s performance during the reporting period. The letter will also provide information about the disbursement amount for the next period. This Management Letter (English / French / Spanish) should be prepared and sent to the SR after the submission of the SRs programmatic and financial reports, after all information is verified and finalized. The PR will inform the SR about:
- Status of management actions from the previous reporting period(s);
- Management issues identified during the reporting period; and
- Corrective actions required to address observed issues including deadlines.
Loading resources